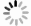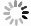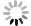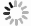Heart disease identification based on boosted decision tree
-
摘要: 基于高能物理数据分析的ROOT框架下的梯度提升决策树(BDTG)模型,提出一种多变量分析法用于心脏病鉴别。通过大量的临床数据,分析变量的各种复杂关系提高心脏病鉴别的准确性和可靠性。使用Kaggle开源心脏病数据集,结果表明,模型在BDTG响应值为−0.4~0.5时,没有出现错误鉴别情况。当BDTG响应值的截断为−0.6或0.6时,模型的准确率、查准率、查全率和F1分数达到98%以上。该模型在心脏病诊断方面具有较高的准确性和可靠性,不仅为心脏病预测提供新视角和方法,也为其他疾病的机器学习预测研究提供参考。Abstract: A gradient boosting decision tree (BDTG) model based on high-energy physics data analysis in ROOT framework was proposed for the identification of heart disease using a multivariate analysis method. Through a large amount of clinical data, the aim is to analyze the various complex relationships of variables to improve the accuracy and reliability of heart disease differentiation. Using the Kaggle open-source heart disease dataset, the results showed that the model did not exhibit any erroneous discrimination when the BDTG responsevalues range between between −0.4 and 0.5. In addition, when the truncation of BDTG response values is −0.6 or 0.6, the model still maintained above 98% in accuracy, precision, recall and F1 scores. Therefore, the model has high accuracy and reliability in the diagnosis of heart disease. This study not only provides new perspectives and methods for predicting heart disease, but also serves as a reference for machine learning prediction research on other diseases.
-
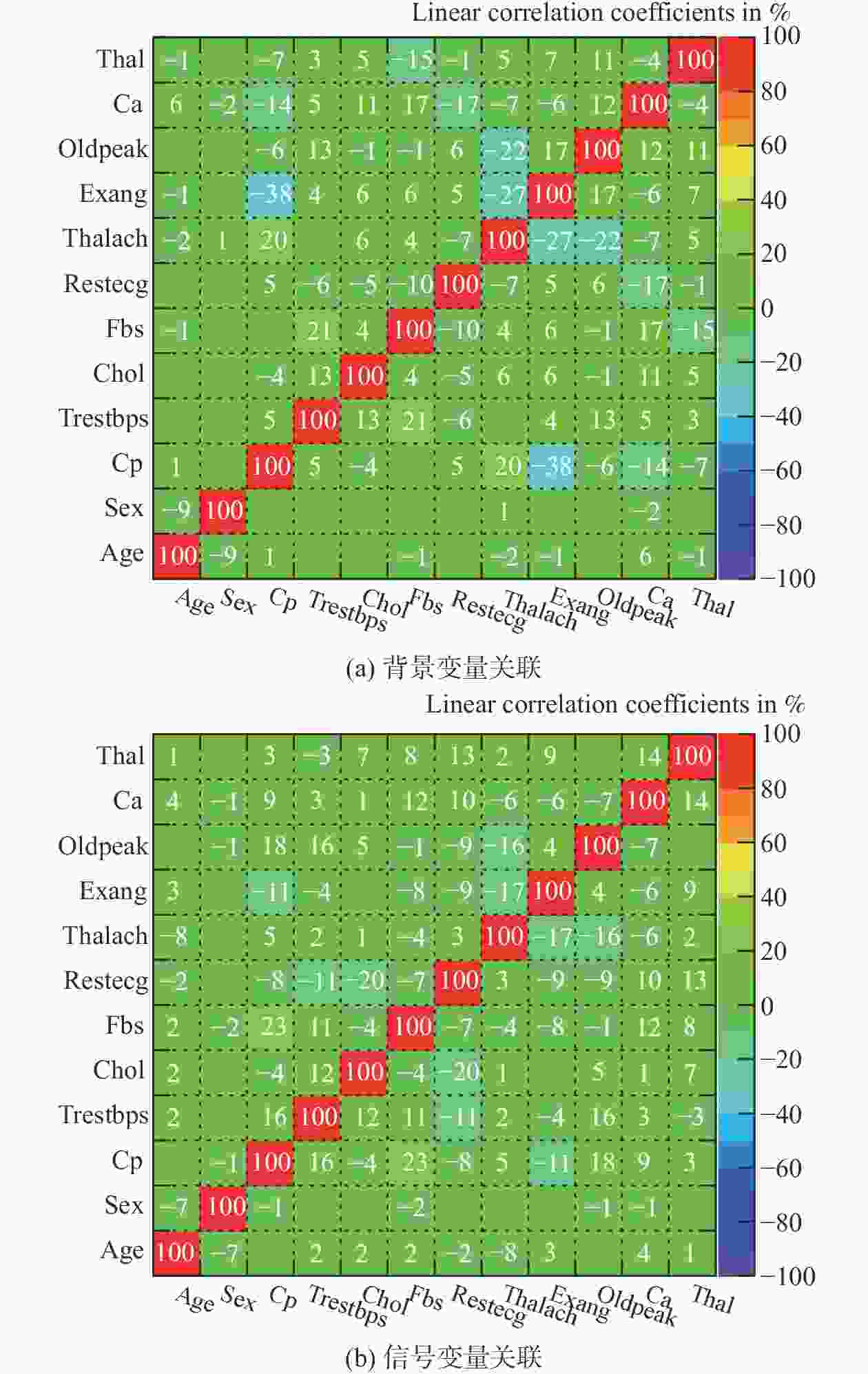
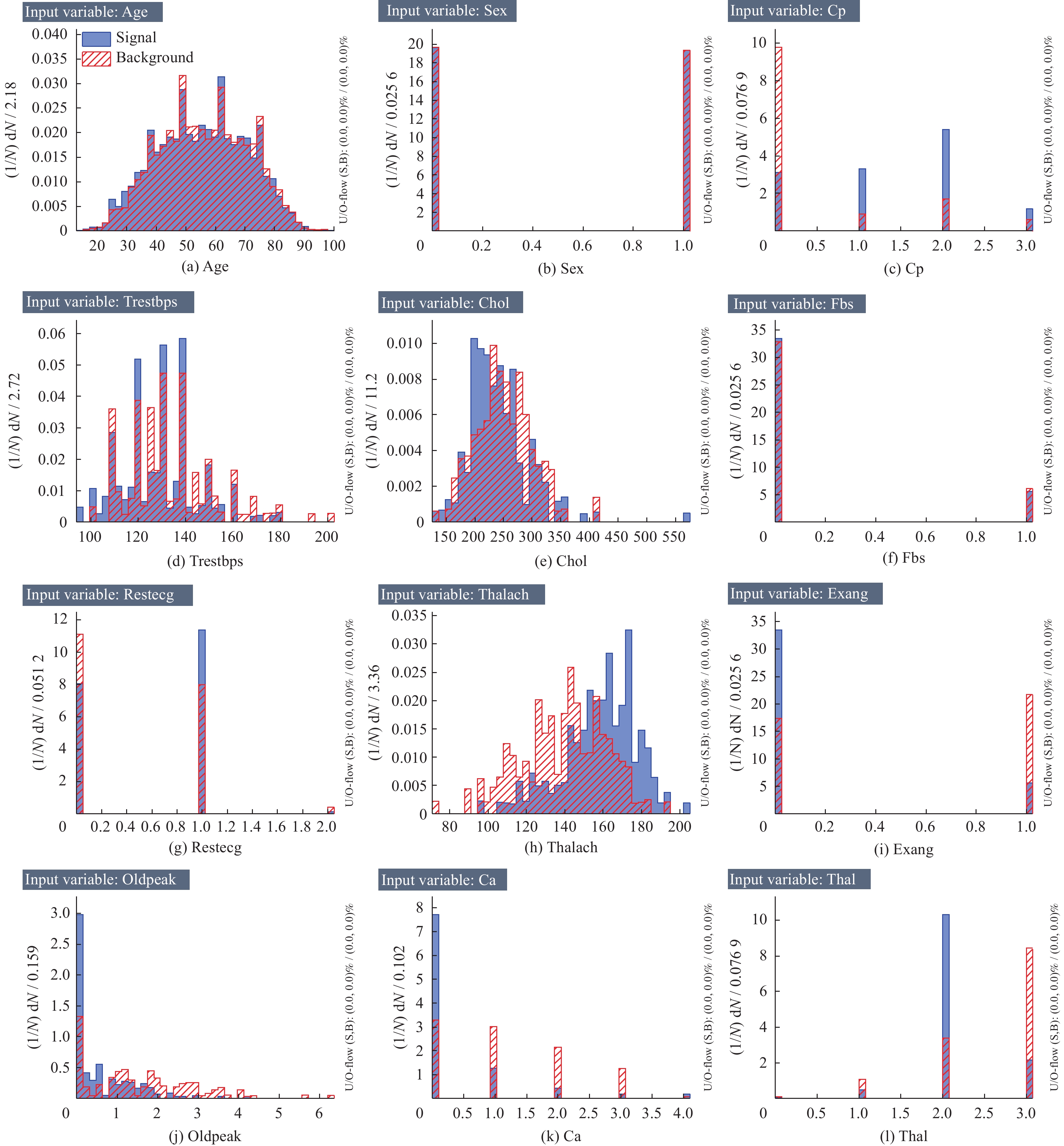
表 1 数据集特征变量
Table 1. Dataset feature variable
序号 特征 描述 1 Age 年龄 2 Sex 性别 3 Cp 胸痛类型 4 Trestbps 静息血压/(mm·Hg−1) 5 Chol 胆固醇/(mg·dL−1) 6 Fbs 空腹血糖 7 Restecg 静息心电图 8 Thalach 最大心率 9 Exang 运动诱发性心绞痛 10 Oldpeak ST抑制 11 Ca 主要血管数量 12 Thal 地中海贫血 13 Target 心脏病 表 2 4种预测结果类别的具体描述
Table 2. Description of four prediction result categories
类型 描述 TP(真正例) 真实值为1,预测值为1 TN(真负例) 真实值为0,预测值为0 FP(假正例) 真实值为0,预测值为1 FN(假负例) 真实值为1,预测值为0 表 3 BDTG调节参数
Table 3. BDTG tuning parameters
参数 含义 设置 Ntree 树的数量 1000 BoostType 提升算法类型 Gradient Shrinkage GradientBoost算法学习率 0.1 nCuts 节点切割优化过程步骤数 20 MaxDepth MaxDepth 决策树最大深度 表 4 特征变量影响排序
Table 4. Influence of characteristic variable ranking
排序 特征变量 影响程度 1 Chol 0.146 2 Trestbps 0.142 3 Thalach 0.125 4 Oldpeak 0.115 5 Ca 0.086 表 5 BDTG 响应在不同值截断的模型表现评价
Table 5. BDTG performance measurements
BDTG响应 查准率/% 查全率/% F1分数/% −0.6 98.84 100 99.42 −0.5 99.88 100 99.94 −0.45 99.97 100 99.98 −0.4~0.5 100 100 100 0.55 100 99.86 99.93 0.6 100 99.39 99.69 -
[1] 马丽媛, 王增武, 樊静, 等. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》要点解读[J] . 中国全科医学,2023,26(32):3975 − 3994. [2] 李秀清. 心脑血管疾病的危险因素及预防方法分析[J] . 亚太传统医药,2012,8(1):179 − 181. [3] 闫一鸣, 欧阳文斌, 张凤文, 等. 中国先天性心脏病介入治疗现状与展望[J] . 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2022,29(10):1243 − 1253. [4] 梅宏, 杜小勇, 金海, 等. 大数据技术前瞻[J] . 大数据,2023,9(1):1 − 20. [5] 肖博达, 周国富. 人工智能技术发展及应用综述[J] . 福建电脑,2018,34(1):98 − 99 [6] 陈蒙蒙, 方振红, 涂文怡, 等. 基于Logistic回归模型的心脏病预测模型构建及效果分析[J] . 医院管理论坛,2022,39(2):32 − 35. [7] 王成武, 郭志恒, 晏峻峰. 改进的支持向量机在心脏病预测中的研究[J] . 计算机技术与发展, 2022, 32(3): 175−179. [8] 谭朋柳, 徐光勇, 张露玉, 等. 基于卷积神经网络和Adaboost的心脏病预测模型[J] . 计算机应用,2023,43(S1):19 − 25. [9] 赵金超, 李仪, 王冬, 等. 基于优化的随机森林心脏病预测算法[J] . 青岛科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,42(2):112 − 118. [10] 刘柃伶, 黄学德. 基于XGBoost和SHAP的心脏病影响因素分析[J] . 信息与电脑(理论版),2024,36(6):68 − 70. [11] ALAN S C, WESLEY D, BENJAMIN F, et al. Boosted decision trees in the era of new physics: a smuon analysis case study[J] . Journal of High Energy Physics,2021(2022):1 − 15. [12] NIKOLAY K,OLEG S. Method for improving gradient boosting learning efficiency based on modified loss functions[J] . Automation and Remote Control,2022(83):1935 − 1943. [13] ANDREAS T. ConfusionVis: comparative evaluation and selection of multi-class classifiers based on confusion matrices[J] . Knowledge-Based Systems,2022(247):3 − 12. [14] TAFFAZUL C, BISMITA C. Automated cardiovascular disease prediction models: A comparative analysis[J] . EAI Endorsed Transactions on Pervasive Health and Technology,2023(9):1 − 6. [15] RAQUEL S, VERONIKA T, CELIA O, et al. Balancing risk and profit: Predicting the performance of potential new customers in the insurance industry[J] . Journal cf Information Science,2024(15):546. [16] ASADA Y. Evaluation of the performance of a machine learning based atrial fibrillation screening algorithm using an oscillometric blood pressure monitor[J] . Scientific Reports,2024(14):1 − 18. [17] DU S S, QIU T, LI L Q, et al. Application of multi-gradient boosting tree in drug identification[J] . Computer Science and Exploration,2020(14):260 − 273. [18] SHAIMAA M, MOHAMED G, GAMAL F, et al. Cardiovascular disease prediction using modified version of resnet-50 model[C] //Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Computer Theory and Applications (ICCTA). Location: IEEE, 2022. -





 下载:
下载: