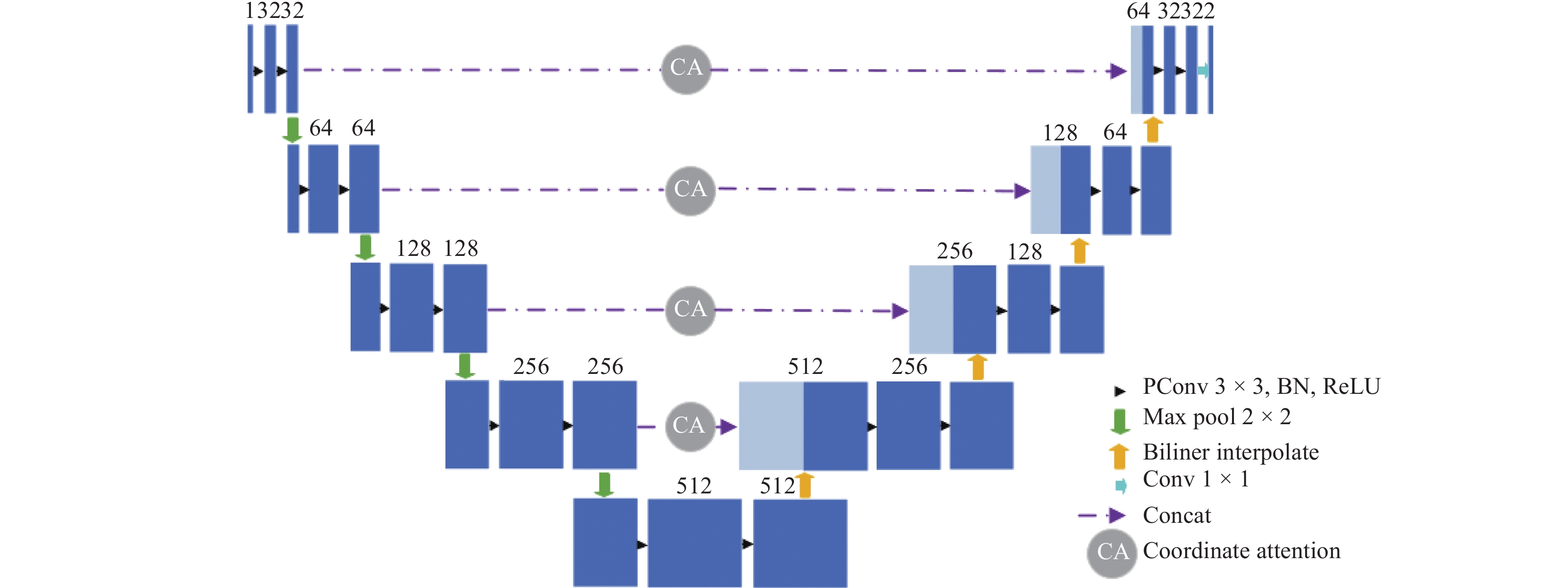
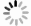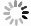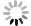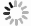Segmentation of lung tumors based on PCU-Net
-
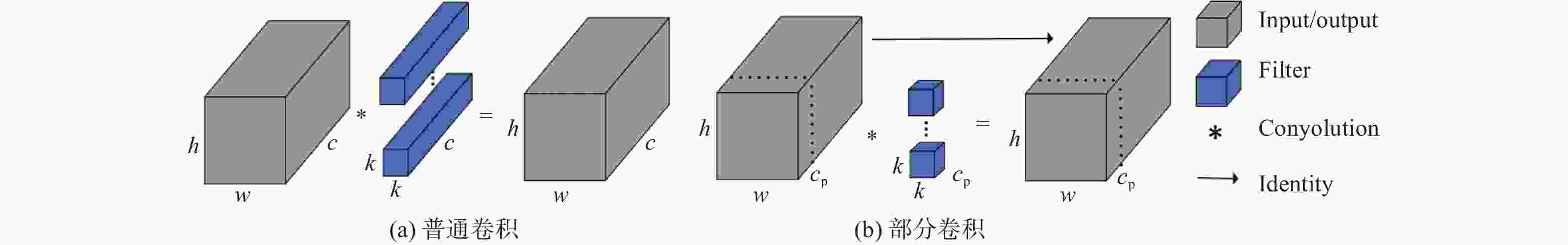
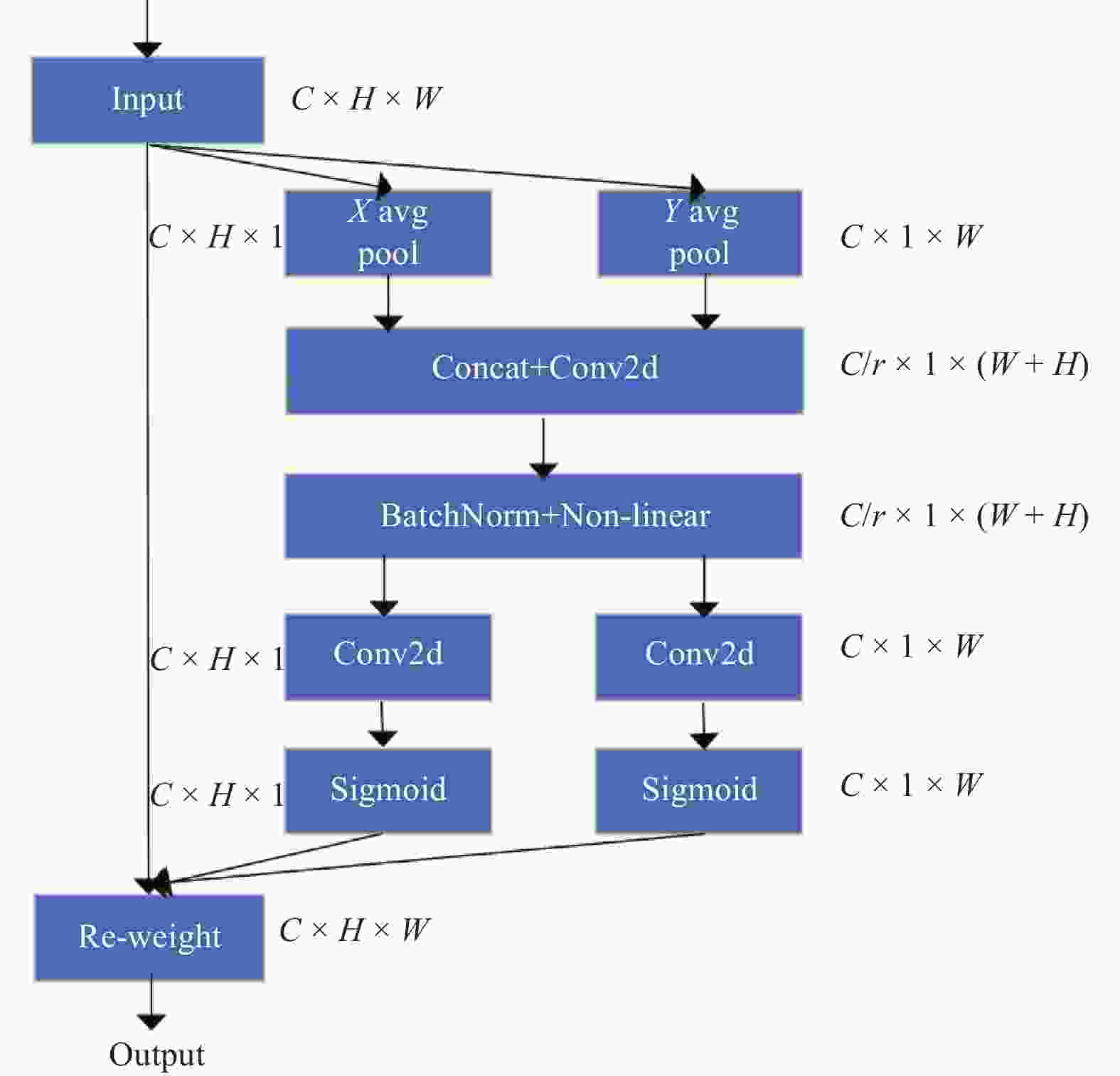
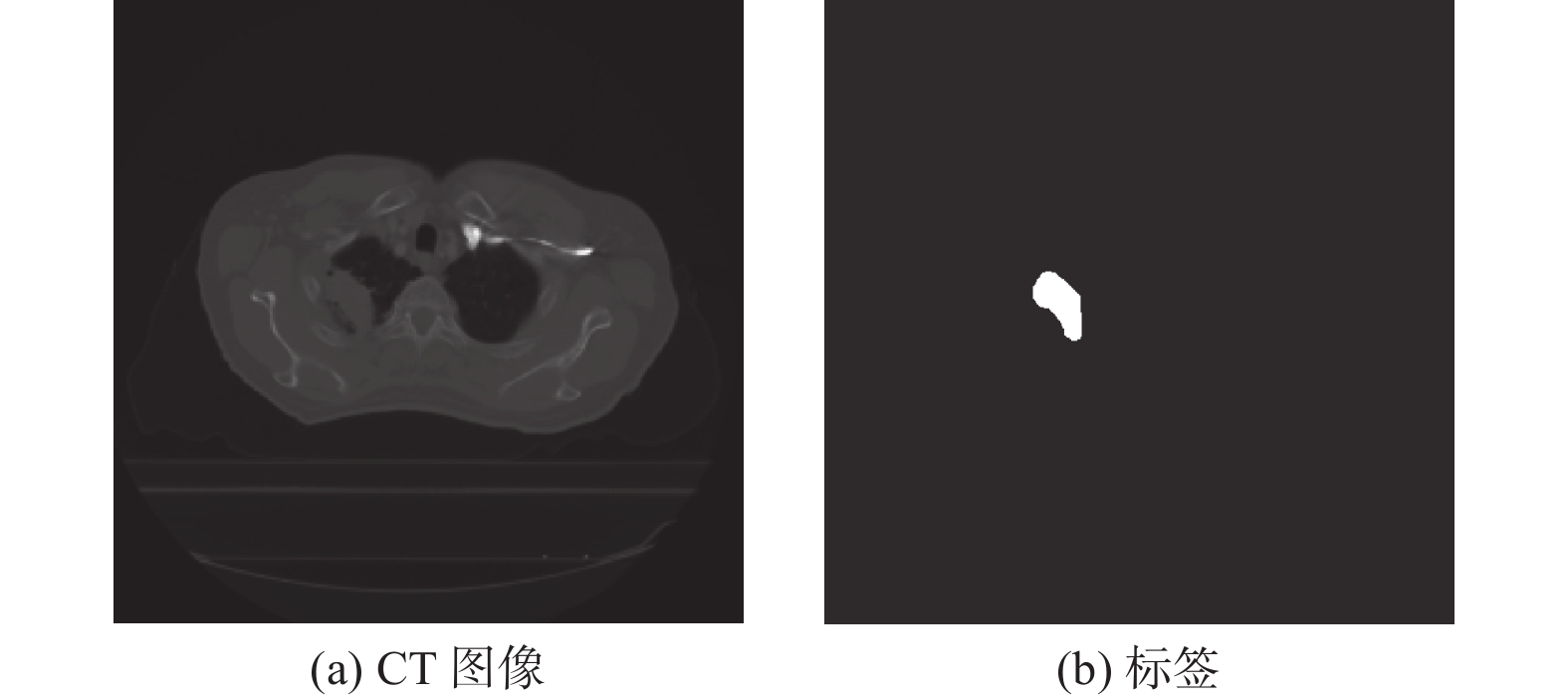
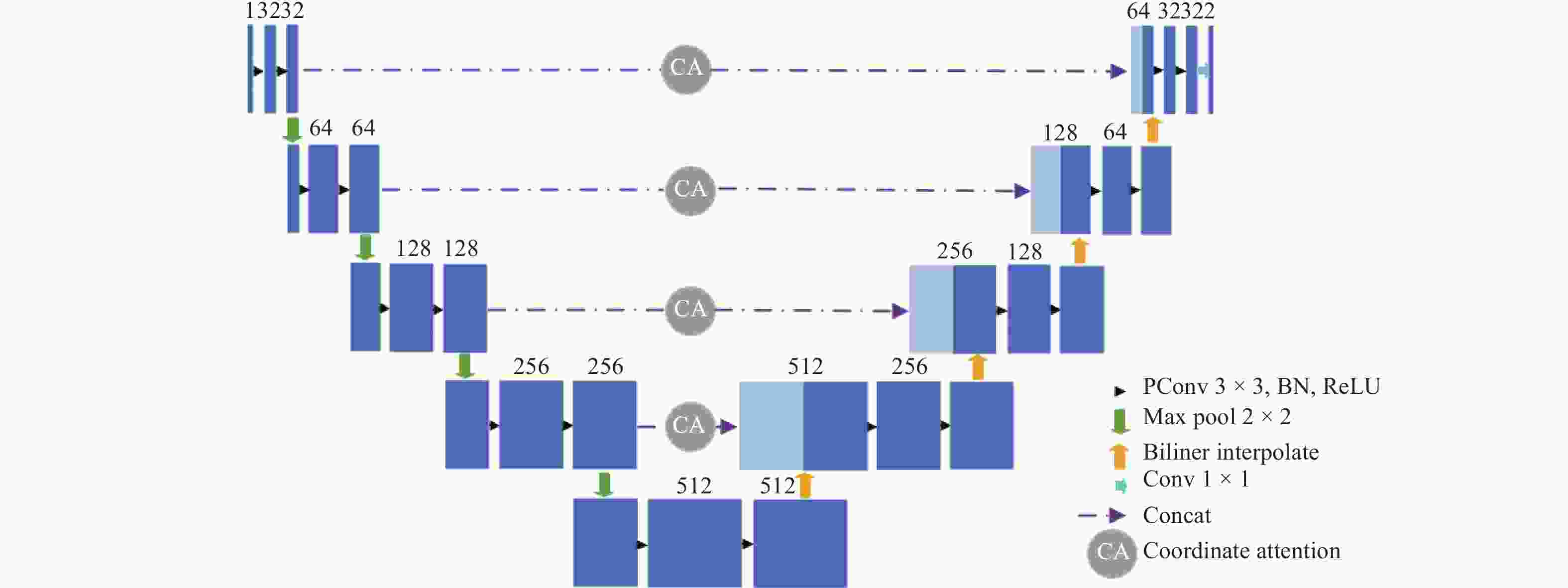
摘要: 深度学习技术可辅助医生进行肿瘤的精准分割。但肺肿瘤与周围组织界限不清楚,现有方法存在分割边缘模糊、模型参数量大等问题。提出一种对轻量级肺肿瘤分割的部分卷积坐标注意力U-net(partial convolution coordinate attention U-net,PCU-Net)算法。引入部分卷积降低模型参数量,同时提升模型特征提取的能力。在U-Net跳跃链接处添加坐标注意力模块,使网络更精准获取肿瘤的位置信息,提高分割精度。研究结果表明,改进的PCU-Net在参数量减少58.57%的同时,Dice值、IoU和Recall分别提高4.22%、4.26%和6.82%。将PCU-Net模型与其他语义分割模型对比显示,PCU-Net的Dice值比其他模型高出3~6百分点。Abstract: Deep learning techniques can assist doctors in precise tumor segmentation. However, existing methods often suffer from issues such as fuzzy segmentation edges and large model parameter counts due to the unclear boundaries between lung tumors and surrounding tissues. A partial convolution coordinate attention U-net (PCU-Net) algorithm for lightweight lung tumor segmentation was proposed. The partial convolution was introduced to reduce model parameters and enhance feature extraction capability. The coordinate attention module was added at skip connection of PCU-Net, so that more precise localization of tumors was achieved by network and segmentation accuracy was improved. The research result shows that the improved PCU-Net can reduce model parameters by 58.57% while increase Dice coefficient, Intersection over Union (IoU) and Recall by 4.22%, 4.26% and 6.82%, respectively. The comparison between PPU-Net and other semantic segmentation models shows that Dice coefficient of PCU-Net is 3-6 percentage points higher than that of other models.
-
表 1 不同算法的分割结果
Table 1. Segmentation results of different algorithms
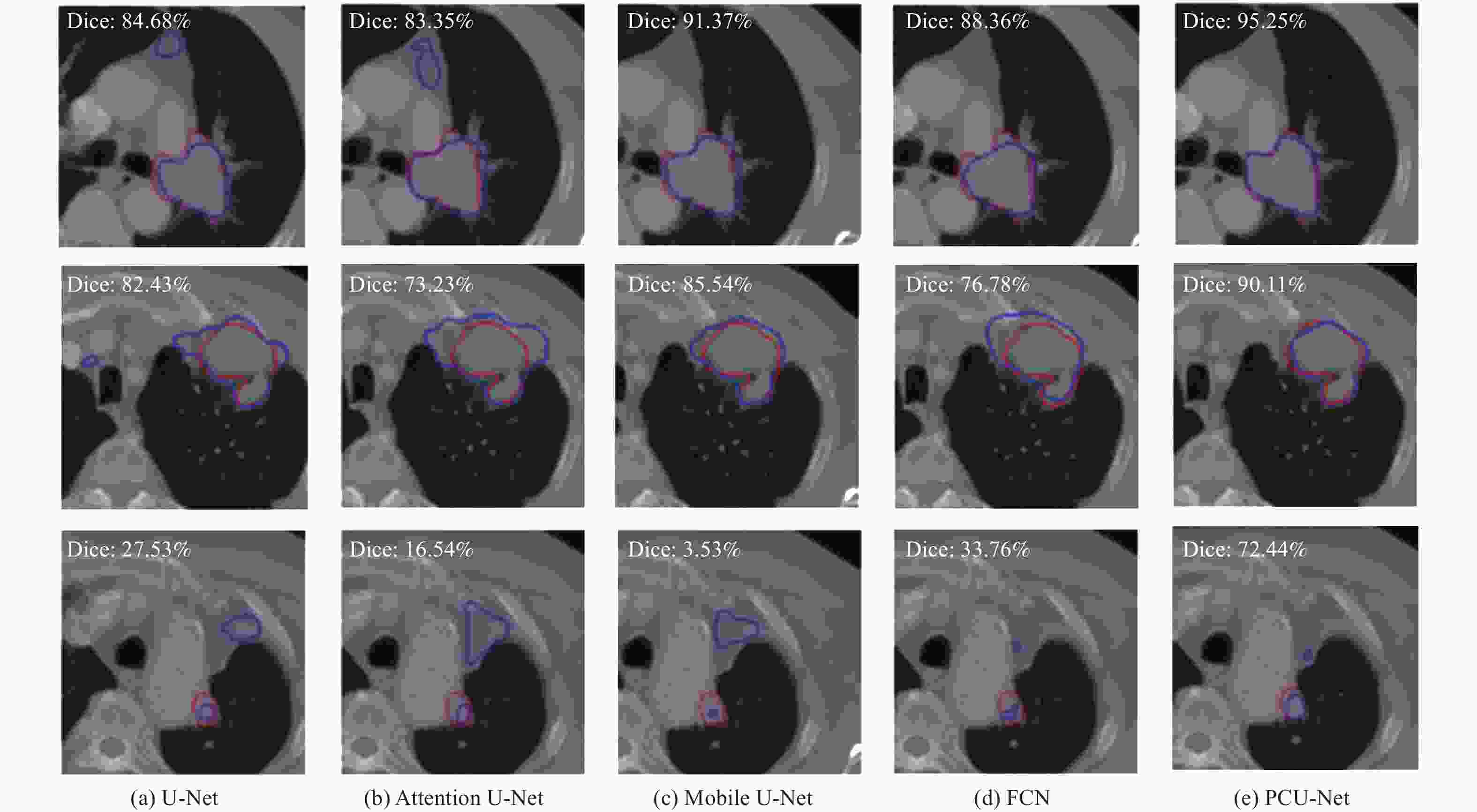
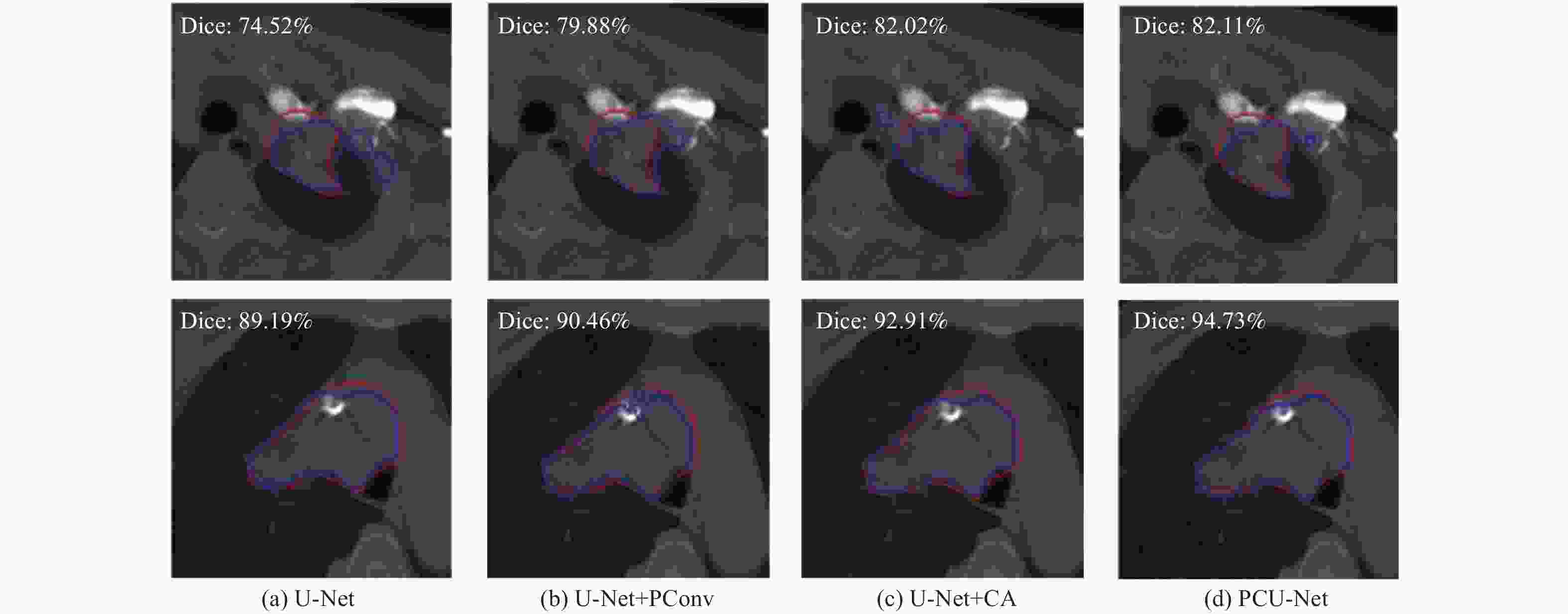
% 模型 Dice IoU Recall U-Net 68.94 57.65 69.53 Attention U-Net 68.71 57.29 72.38 Mobile U-Net 66.20 55.82 67.49 FCN 68.85 57.67 68.60 PCU-Net 73.16 61.91 76.35 表 2 消融试验
Table 2. Ablation experiment
模型 Dice IoU Recall U-Net+PConv 71.84 60.44 74.39 U-Net+CA 71.21 59.31 75.60 PCU-Net 73.16 61.91 76.35 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J] . CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians,2021,71(3):209 − 249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] SOLTANI-NABIPOUR J, KHORSHIDI A, NOORIAN B. Lung tumor segmentation using improved region growing algorithm[J] . Nuclear Engineering and Technology,2020,52(10):2313 − 2319. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2020.03.011 [3] RAKESH S, MAHESH S. Nodule segmentation of lung CT image for medical applications[J] . Global Transitions Proceedings,2021,2(1):80 − 83. doi: 10.1016/j.gltp.2021.01.011 [4] VORONTSOV E, ABI-JAOUDEH N, KADOURY S. Metastatic liver tumor segmentation using texture-based omni-directional deformable surface models[C] //proceedings of the 6th International Workshop ABDI 2014. Cham: Springer, 2014: 74−83. [5] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J] . IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence , 2015, 39(4): 640−651. [6] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C] //Proceedings of International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Munich: Springer International Publishing, 2015: 234−241. [7] MILLETARI F, NAVAB N, AHMAD SA. V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C] //Proceedings of 2016 the Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 565−571. [8] OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, FOLGOC LL, et al. Attention U-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas[C] //Proceedings of IEEE on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018. [9] ZHOU Z, SIDDIQUEE M M, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. Unet ++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation[J] . IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2019,39(6):1856 − 1867. [10] CAO H, WANG Y, CHEN J, et al. Swin-Unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation[J] . 2021. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2105.05537. [11] ZHOU T, DONG Y, LU H, et al. APU-Net: An attention mechanism parallel U-Net for lung tumor segmentation[J] . BioMed Research International , 2022, 2022, 5303651. [12] JIANG J, HU Y C, LIU C J, et al. Multiple resolution residually connected feature streams for automatic lung tumor segmentation from CT images[J] . IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2019,38(1):134 − 144. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2857800 [13] HOSSAIN S, NAJEEB S, SHAHRIYAR A, et al. A pipeline for lung tumor detection and segmentation from CT scans using dilated convolutional neural networks[C] //Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Brighton: IEEE, 2019: 1348−1352. [14] CHEN J, KAO S, HE H, et al. Run, don't walk: Chasing higher FLOPs for faster neural networks[C] //Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Vancouver: IEEE, 2023: 12021−12031. [15] HOU Q, ZHOU D, FENG J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C] //Proceedings of Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. Nashville: IEEE, 2021: 13713−13722. -




 下载:
下载: